J1-Envs: Interactive Legal Environments
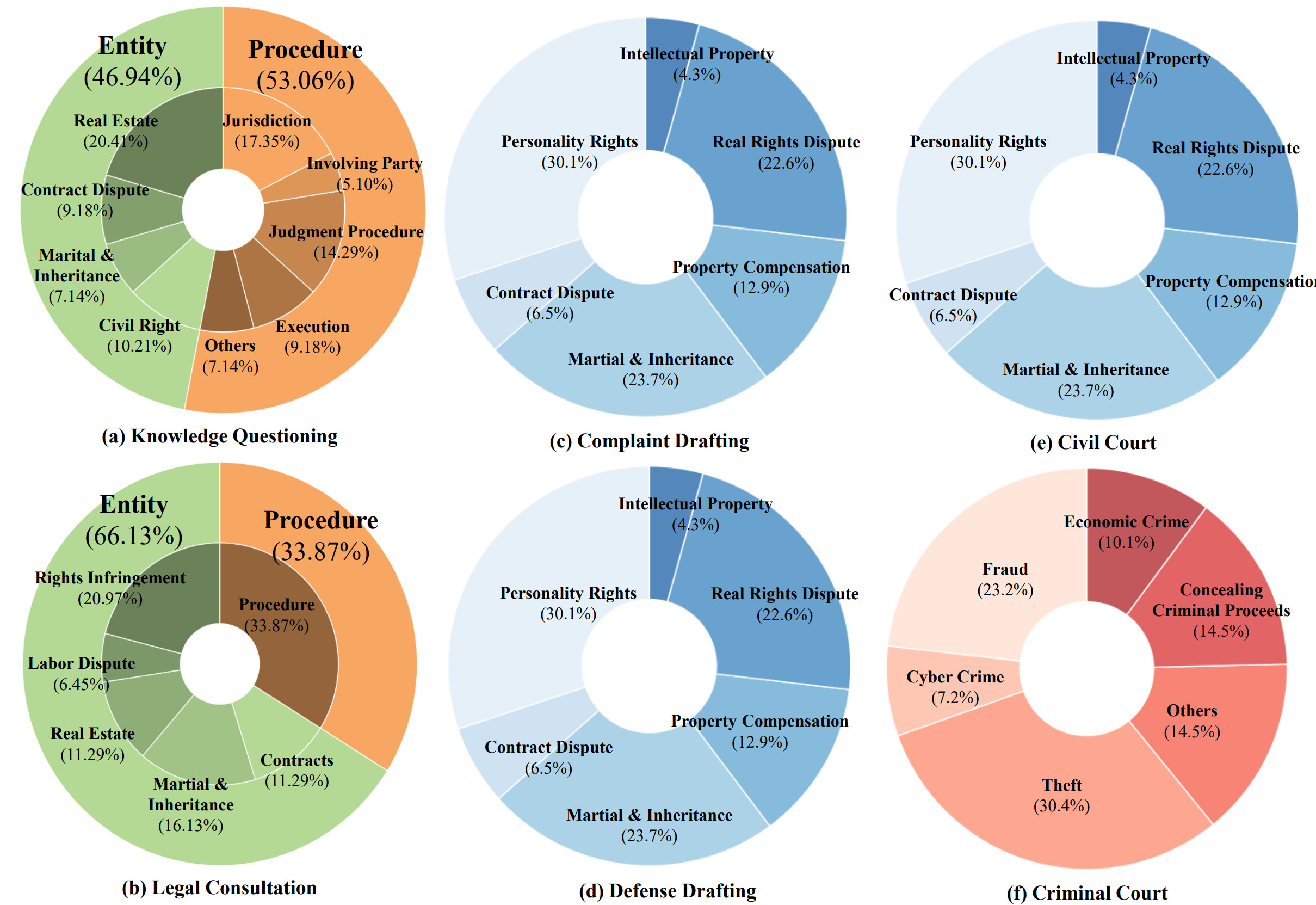
J1-Envs consists of six environments and could be categorized into three levels based on environmental complexity (role diversity, interaction demands, and procedural difficulty):
J1-Eval: Holistic Legal Agent Evaluation
Considering the distinct characteristics of each legal task, J1-Eval provides a set of task-specific and fine-grained metrics to evaluate agent capabilities within our constructed environments with either rule-based or model-based methods.
The contributions of our paper are as follows:
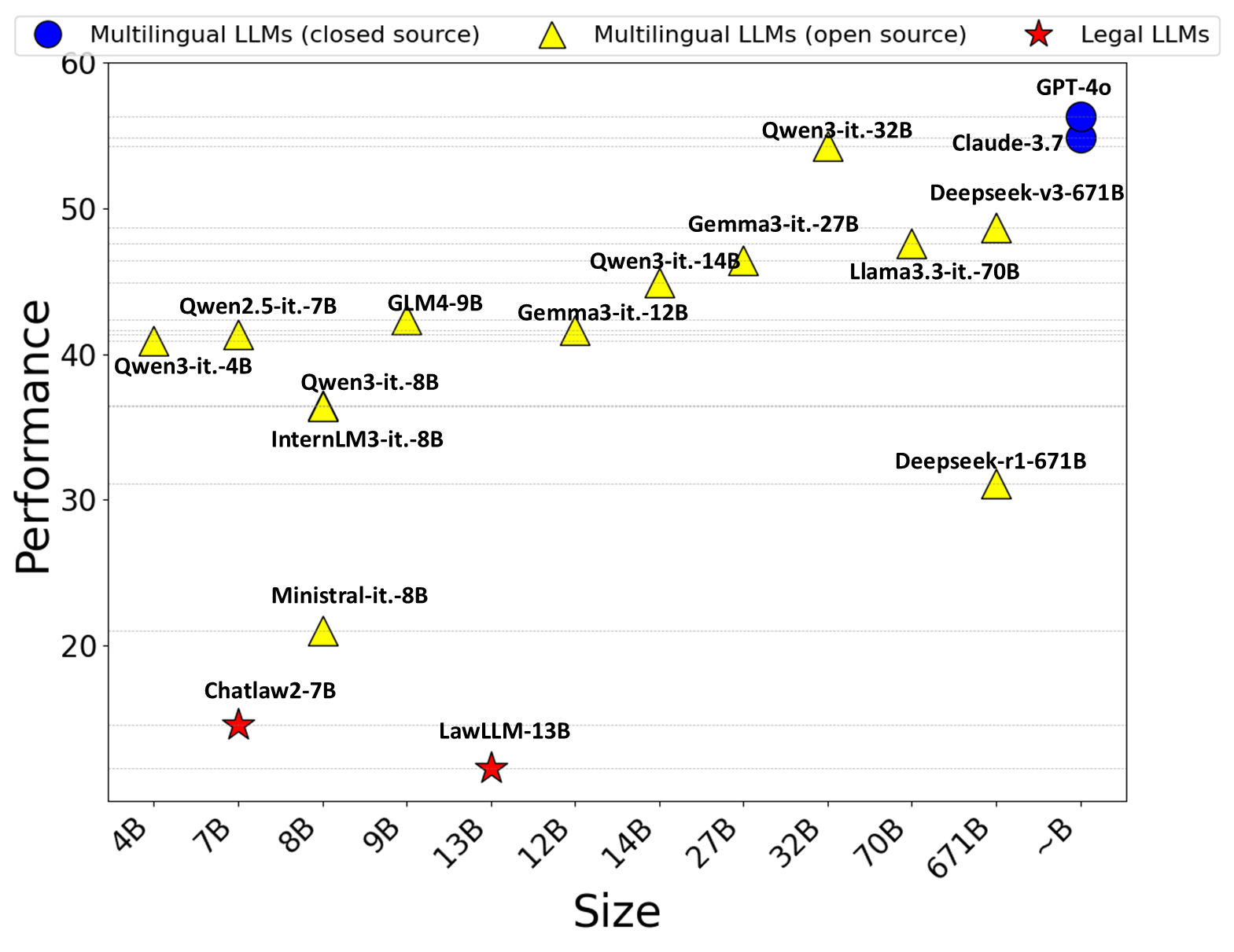
We conduct extensive experiments on 17 LLM agents, including proprietary models, open-source models, and legal-specific models.
Overall performance ranking: GPT-4o achieves the best performance, showing strong legal intelligence. Qwen3-Instruct-32B demonstrates performance beyond expectations, surpassing the Deepseek series. Although the legal-specific LLMs perform comparably to the GPT series on existing legal benchmarks, they exhibit significantly weaker performance in our setting, falling behind even smaller models.
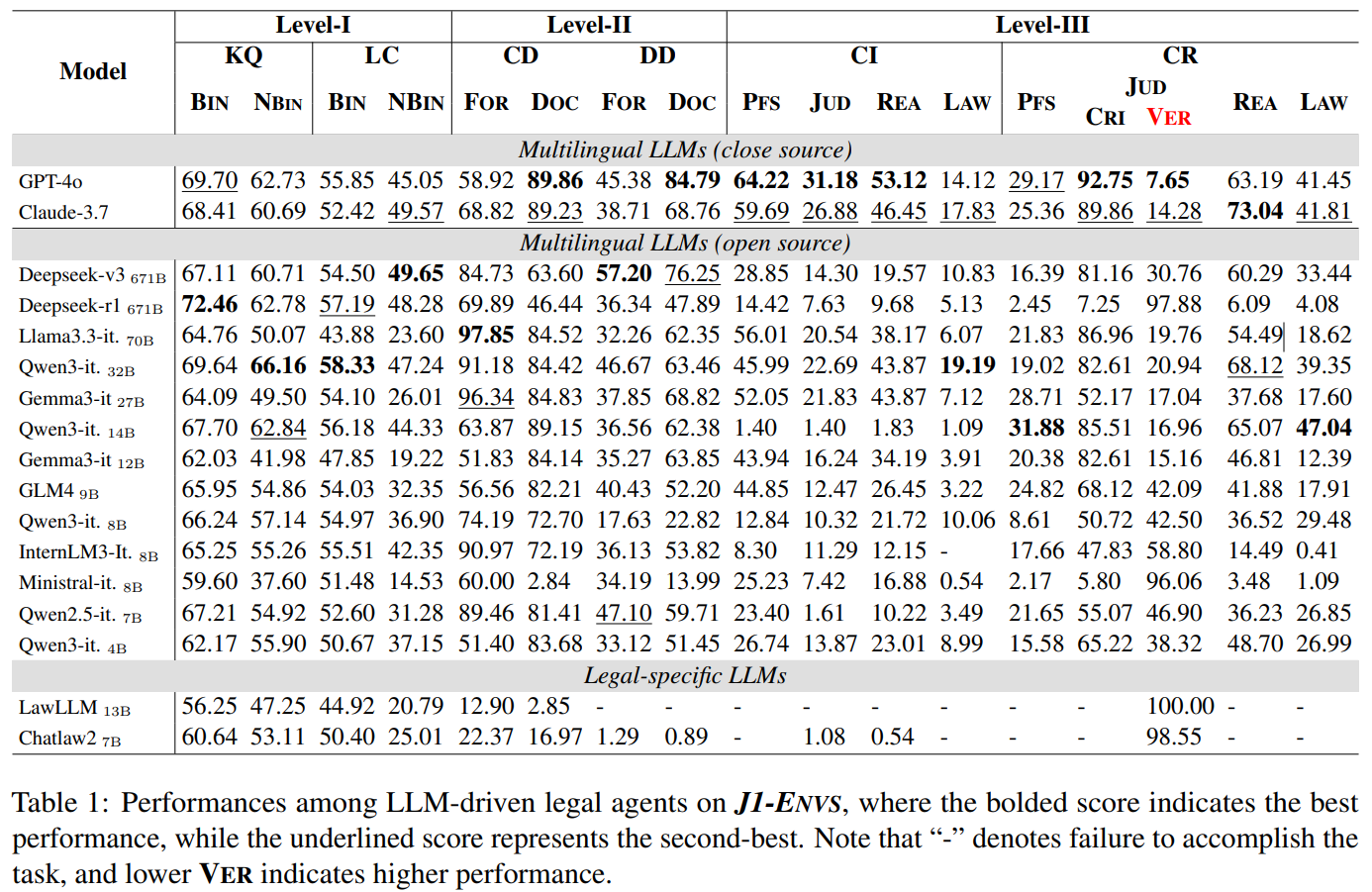
Performance at different levels: Both general and legal-specific models perform relatively well in Level I. However, their performance drops in Level II and Level III, which require proactive engagement and rigorous procedural compliance.
Can LLMs drive J1-ENVS? Both GPT-4o and human rate the consistency between each role's profile and its behavior on a scale of 1 to 10. The ratings(Figure (a)) remain consistently high and stable, which validates the reliability and effectiveness of our environment.
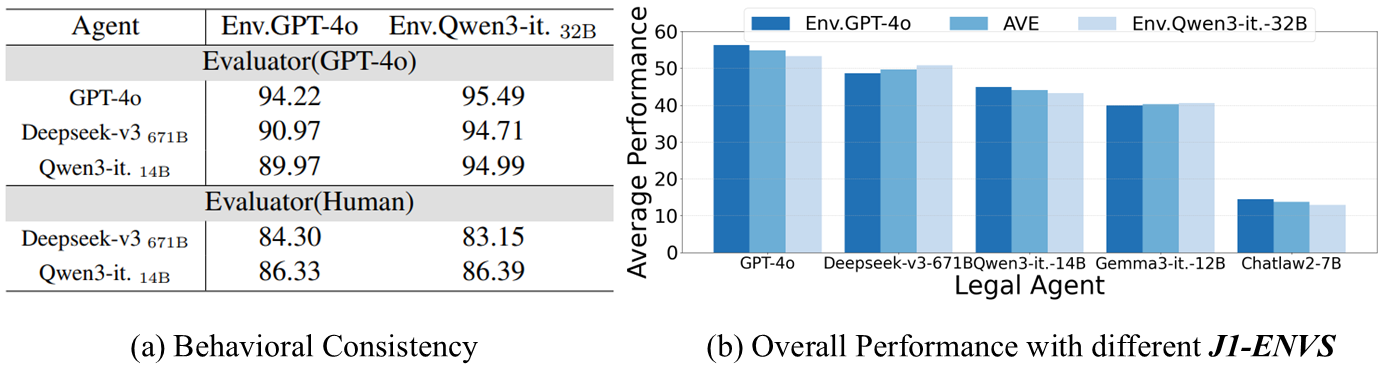 We then employ Qwen3-Instruct-32B to drive our environment, and find that the relative performance differences and rankings(Figure (b)) among agents remain consistent across various environments, further validating the robustness of our framework.
We then employ Qwen3-Instruct-32B to drive our environment, and find that the relative performance differences and rankings(Figure (b)) among agents remain consistent across various environments, further validating the robustness of our framework.
@article{jia2025readyjuristonebenchmarking,
author = {Zheng Jia and Shengbin Yue and Wei Chen and Siyuan Wang and Yidong Liu and Yun Song and Zhongyu Wei},
title = {Ready Jurist One: Benchmarking Language Agents for Legal Intelligence in Dynamic Environments},
year = {2025},
journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2507.04037},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.04037}
}